EpiCypher是一家為表觀遺傳學和染色質(zhì)生物學研究提供高質(zhì)量試劑和工具的專業(yè)制造商�。EpiCypher推出的ChIP級別的Histone H3K27ac Antibody符合EpiCypher的“SNAP-ChIP? Certified”標準,用于ChIP實驗中的特異性和有效靶標富集(整板的交叉反應性<20%�����,靶標輸入的回收率>5%)�����。組蛋白H3是核小體中存在的四種蛋白質(zhì)之一��,核小體是染色質(zhì)的基本重復亞基����,有147個堿基對的DNA纏繞在核心組蛋白(H2A、H2B����、H3和H4)的八聚體上�����。該抗體與H3K27ac結合���,并且在EpiCypher SNAP-ChIP K-AcylStat Panel(EpiCypher 19-3001)中未檢測到與其他賴氨酸酰化的顯著交叉反應性�����。在S28(H3K27acS28ph)磷酸化的情況下����,抗體與H3K27ac的結合在ChIP中受到不同程度的抑制(圖3)��。
產(chǎn)品詳情
反應種屬: Human, Mouse, Wide Range (Predicted)
宿主來源: Mouse
實驗應用: ChIP, ICC/IF
免疫原: A synthetic peptide corresponding to histone H3 acetylated at lysine 27
克隆性: Monoclonal
保存溫度: Stable for 1 year at -20°C from date of receipt
運輸溫度: Frozen cold packs.
產(chǎn)品形式: Protein A affinity-purified antibody in PBS pH 7.4, 0.05% sodium azide
驗證數(shù)據(jù)
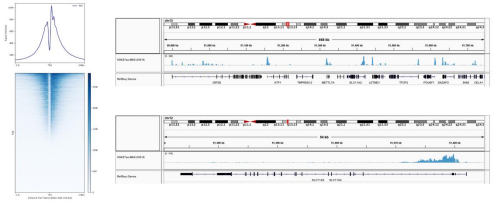 |
Figure 1:Representative SNAP-ChIP-seq results:?Cumulative histogram plot and heatmap of signal intensity depict H3K27ac ChIP-seq data aligned to annotated transcription start sites (TSS, +/- 3.0 kb; left). Two representative genomic regions depicting H3K27ac peak structure and distribution are shown (right). |
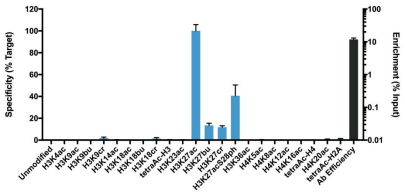 |
Figure 2: SNAP-ChIP-qPCR data. Histone H3K27ac antibody (3 μg) was tested in a native ChIP experiment using chromatin from K562 cells (3 μg) with the SNAP-ChIP K-AcylStat Panel (EpiCypher 19-3001) spiked-in prior to micrococcal nuclease digestion. Specificity (left y-axis) was determined by qPCR for the DNA barcodes corresponding to modified nucleosomes in the SNAP-ChIP panel (x-axis). Black bar represents antibody efficiency (right yaxis; log scale) and indicates percentage of the target immunoprecipitated relative to input. Error bars represent mean ± SEM in replicate ChIP experiments. |
訂購詳情
貨號 | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | 規(guī)格 |
13-0045 | Histone H3K27ac Antibody, SNAP-ChIP? Certified | 50 μg |

如需了解更多詳細信息或相關產(chǎn)品�,請聯(lián)系EpiCypher中國授權代理商-欣博盛生物?
全國服務熱線: 4006-800-892 ? ? ??郵箱: market@neobioscience.com?
深圳: 0755-26755892 ? ? ? ??北京: 010-88594029 ???????????
廣州:020-87615159????????? ?上海: 021-34613729
代理品牌網(wǎng)站: www.smblzp.com?
自主品牌網(wǎng)站: www.neobioscience.net