BioXcell熱銷(xiāo)產(chǎn)品推薦--InVivoMab anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)
?
產(chǎn)品描述:
BioXcell InVivoMab anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)?10F.9G2單克隆抗體與小鼠PD-L1(也稱(chēng)為B7-H1或CD274)反應(yīng)���。PD-L1是屬于Ig超家族的B7家族的I型跨膜蛋白,分子量為40kDa����。PD-L1在T淋巴細(xì)胞、B淋巴細(xì)胞��、NK細(xì)胞��、樹(shù)突狀細(xì)胞以及IFNγ刺激的單核細(xì)胞��、上皮細(xì)胞和內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞上表達(dá)�。PD-L1與CD4和CD8胸腺細(xì)胞以及活化的T和B淋巴細(xì)胞和骨髓細(xì)胞上的受體PD-1結(jié)合。PD-L1與PD-1的結(jié)合導(dǎo)致抑制TCR介導(dǎo)的T細(xì)胞增殖和細(xì)胞因子產(chǎn)生�����。PD-L1被認(rèn)為在腫瘤免疫逃避中起著重要作用��。誘導(dǎo)的PD-L1表達(dá)在許多腫瘤中很常見(jiàn)����,并導(dǎo)致腫瘤細(xì)胞對(duì)CD8 T細(xì)胞介導(dǎo)的裂解的抗性增加�。在黑色素瘤的小鼠模型中���,可以通過(guò)用阻斷PD-L1和PD-1之間相互作用的抗體處理來(lái)暫時(shí)腫瘤生長(zhǎng)��。BioXcell InVivoMab anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1)?10F.9G2抗體已被證明可以阻斷PD-L1和PD-1之間以及PD-L1和B7-1之間的相互作用(CD80)。
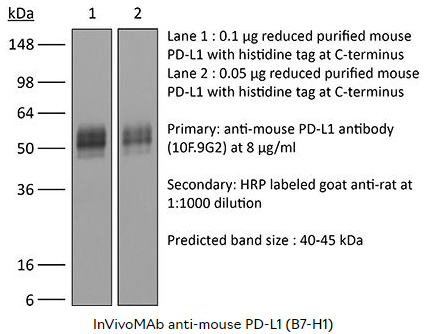 ?
?
產(chǎn)品詳情:
| 產(chǎn)品名稱(chēng) | InVivoMAb anti-mouse PD-L1 (B7-H1) |
產(chǎn)品貨號(hào) | BE0101 |
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格 | 1/5/25/50/100mg |
反應(yīng)種屬 | Mouse |
克隆號(hào) | 10F.9G2 |
同種型 | Rat IgG2a, κ |
免疫原 | Mouse CD274 |
實(shí)驗(yàn)應(yīng)用 | in vivo PD-L1 blockade Immunofluorescence Immunohistochemistry (frozen) Flow cytometry Western blot |
產(chǎn)品形式 | PBS, pH 6.5,Contains no stabilizers or preservatives |
純度 | >95%, Determined by SDS-PAGE |
無(wú)菌處理 | 0.2 μm filtration |
純化方式 | Protein G |
RRID | AB_10949073 |
分子量 | 150 kDa |
保存條件 | 抗體原液保存在4°C��,不能冷凍保存�����。 |
推薦同型對(duì)照 | InVivoMAb rat IgG2b isotype control, anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin(貨號(hào)BE0090) |
推薦抗體稀釋液 | InVivoPure pH 6.5 Dilution Buffer(貨號(hào)IP0065) |
?該產(chǎn)品自上市已被多篇SCI文獻(xiàn)引用�����,品質(zhì)有保證�,以下是部分已發(fā)表的文獻(xiàn)引用:
應(yīng)用 | 文章 |
體內(nèi)PD-L1信號(hào)阻斷 (in vivo PD-L1 blockade) | 1.?Grasselly, C., et al. (2018). 'The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent' Front Immunol 9: 2100. 2.?Stathopoulou, C., et al. (2018). 'PD-1 Inhibitory Receptor Downregulates Asparaginyl Endopeptidase and Maintains Foxp3 Transcription Factor Stability in Induced Regulatory T Cells' Immunity 49(2): 247-263 e247. ? 3.?Jaworska, K., et al. (2015). 'Both PD-1 ligands protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury' J Immunol 194(1): 325-333. 4.?Kim, J., et al. (2015). 'Memory programming in CD8(+) T-cell differentiation is intrinsic and is not determined by CD4 help' Nat Commun 6: 7994. ? 5.?Zander, R. A., et al. (2015). 'PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity' Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641. 6.?Tkachev, V., et al. (2015). 'Programmed death-1 controls T cell survival by regulating oxidative metabolism' J Immunol 194(12): 5789-5800. 7.?Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al. (2015). 'Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer' Nature 520(7547): 373-377. ? |
體內(nèi)PD-L1阻斷,流式細(xì)胞術(shù) (in vivo PD-L1 blockade, Flow Cytometry) | 1.?loulou, M., et al. (2016). 'Follicular regulatory T cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen and derive from naive T cells' Nat Commun 7: 10579. 2.?Ngiow, S. F., et al. (2015). 'A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1' Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811. 3.?Rutigliano, J. A., et al. (2014). 'Highly pathological influenza A virus infection is associated with augmented expression of PD-1 by functionally compromised virus-specific CD8+ T cells' J Virol 88(3): 1636-1651. |
體內(nèi)PD-L1阻斷�����,免疫熒光 (in vivo PD-L1 blockade, Immunofluorescence) | 1.Willimsky, G., et al. (2013). 'Virus-induced hepatocellular carcinomas cause antigen-specific local tolerance' J Clin Invest 123(3): 1032-1043. |
免疫組織化學(xué)(冷凍)��,免疫熒光 (Immunohistochemistry (frozen), Immunofluorescence ) | 1.Riella, L. V., et al. (2011). 'Essential role of PDL1 expression on nonhematopoietic donor cells in acquired tolerance to vascularized cardiac allografts' Am J Transplant 11(4): 832-840. |
?
?
?
?

更多產(chǎn)品詳情請(qǐng)咨詢(xún) BioXcell 中國(guó)授權(quán)代理——欣博盛生物
全國(guó)服務(wù)熱線(xiàn): 4006-800-892 ? ? ??郵箱: market@neobioscience.com?
深圳: 0755-26755892 ? ? ? ??北京: 010-88594029 ???????????
廣州:020-87615159????????? ?上海: 021-34613729
代理品牌網(wǎng)站: www.smblzp.com?
自主品牌網(wǎng)站: www.neobioscience.net