?
?
α-突觸核蛋白與帕金森氏癥的病因與疾病發(fā)展有著密切的聯(lián)系�����。帕金森氏癥 (PD) 是一種神經(jīng)衰退疾病,該疾病患者的大腦中可見α-突觸核蛋白聚集形成路易體�����。α-突觸核蛋白是由SNCA基因表達(dá)的一種分子量為 14-kDa 的蛋白�。目前已知的α-突觸核蛋白的自然狀態(tài)可有很多種:可能是沒有折疊的單體1、折疊的四聚體����、或者是處于和其他寡聚體動態(tài)共存的形式2。在帕金森疾病中�,這些分子量小的α-突觸核蛋白會聚集形成原纖維、纖維以及路易體��,從而導(dǎo)致神經(jīng)元的病變和死亡���。也有其他研究表明寡聚體和原纖維具有神經(jīng)毒性3-6而路易小體可能有神經(jīng)保護(hù)功能7����。?
?
?
 ? ?
|
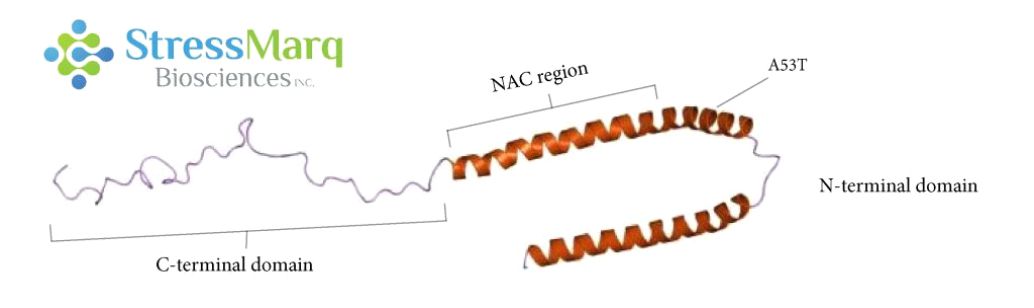
α-突觸核蛋白由三個主要區(qū)域:羧基末端區(qū)域�、NAC區(qū)域、以及氨基末端區(qū)域���。A53T?突變位于氨基末端區(qū)域�����。? |
?
?
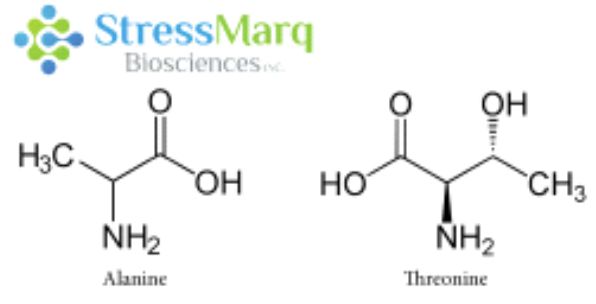
A53T是錯義點突變, 也就是導(dǎo)致了氨基酸的改變:第53個氨基酸由丙氨酸突變?yōu)?/span>蘇氨酸�。該突變是由于SNCA基因 209位置的鳥嘌呤變成了腺嘌呤 (G209A)8�����。A53T 突變與一種常染色體顯性遺傳的早發(fā)型 PD 相關(guān)���,這種 PD 最先發(fā)現(xiàn)于意大利和希臘裔家族8����,也見于一個韓國裔家族9��。 A53T 變異導(dǎo)致該疾病的發(fā)病年齡比較早8��。雖然大部分的 PD 病例是散發(fā)型的�����,并非遺傳病���,而且也不涉及 A53T 突變, 但是研究 A53T 突變可以幫助科研學(xué)者們更好的了解α-突觸核蛋白的聚集和發(fā)展機制���,從而研發(fā)出更好的疾病模型和治療方案���。?
?
?
 ? ?
|
丙氨酸和蘇氨酸有相似的結(jié)構(gòu),但是α-突觸核蛋白中的丙氨酸替換成蘇氨酸對α突觸核蛋白的纖維原聚集有很大的作用���。? |
?
?
A53T 變異只涉及到單一氨基酸改變�,而且丙氨酸和蘇氨酸結(jié)構(gòu)上非常相近�����,那么為什么A53T突變型有這么強的聚集效果呢��?這是因為A53T和其他致病突變都發(fā)生在α-突觸核蛋白的氨基末端����,理論模型顯示 A53T 突變會使α-突觸核蛋白的 NAC 區(qū)域和氨基或羧基區(qū)域的長程相互作用消失,導(dǎo)致 beta折疊的加速形成13���。NMR 測量數(shù)據(jù)顯示 A53T 突變可以延長并穩(wěn)定在寡聚化和纖維化中起著重要作用的 beta折疊結(jié)構(gòu)14���。因此A53T 突變型能夠更快聚集alpha突觸核蛋白����,有更明顯的致病效果����。下面的硫黃素T檢測曲線可以明顯看出A53T突變型的聚集效果明顯強于非突變型α-突觸核蛋白。?
?
?
 ? ?
| 硫黃素T是一種熒光染料�,可以綁定富含beta折疊的結(jié)構(gòu),例如α-Syn聚合體����。綁定之后�,硫黃素T光譜會發(fā)生紅移,熒光強度會增強���。A53Tα-Syn蛋白單體(SPR-325)的硫黃素T發(fā)射光曲線顯示了有限的熒光強度增強(相關(guān)于α-Syn蛋白聚合體)�。而10nM活性α-Syn聚合體(SPR-326)與100μm活性α-Syn單體(SPR-325)混合時熒光強度明顯增強�,這是由于聚合體催化了活性單體形成更多聚集體PFFs。ThioflavinTλex=450nm����,λem=485?nm。? |
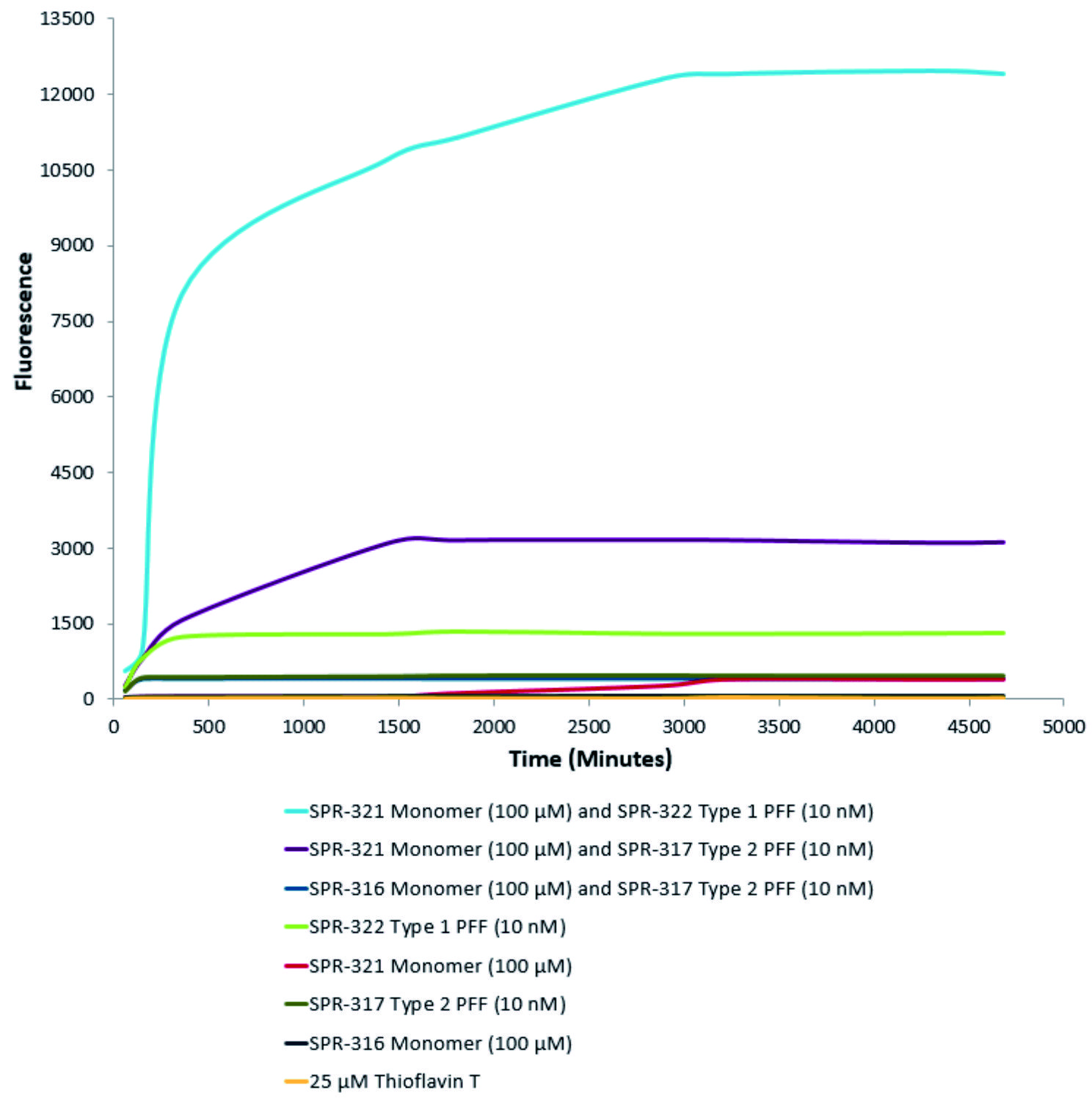 ? ?
| 活性突觸核蛋白(α-Syn)聚合體(SPR-322)催化活性單體(SPR-321)形成新的聚合體�����。硫黃素T是一種熒光染料,可以綁定富含beta折疊的結(jié)構(gòu),例如α-Syn聚合體.綁定之后,硫黃素T光譜會發(fā)生紅移���,熒光強度會增強�����。左側(cè)硫黃素T發(fā)射光曲線展示了四種試驗對象隨時間增強的熒光強度(相關(guān)于α-Syn?蛋白聚合體)�,其中10nM活性α-Syn聚合體(SPR-322)與100μm活性α-Syn單體(SPR-321)混合物熒光增強最明顯��,另外幾組對比分別是活性α-Syn聚合物(SPR-322)�、活性α-Syn單體(SPR-321)以及ThioflavinTλex=450nm,λem=485?nm。? |
?
A35T突變型alpha突觸核蛋白新品上市半價促銷����,活動時間2019年3月1日至4月30日,折扣碼 A35T50����。?
?
?
參考文獻(xiàn):?
1、Fauvet B, et al. alpha-Synuclein in central nervous system and from erythrocytes, mammalian cells, and Escherichia coli exists predominantly as disordered monomer.?J Biol Chem. 2012;287:15345–64.?
2����、Dehay B, Bourdenx M, Gorry P, et al. Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations.?Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(8):855-866.?
3���、Karpinar DP, et al. Pre-fibrillar alpha-synuclein variants with impaired beta-structure increase neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease models.?EMBO J.?2009;28:3256–68.?
4、Winner B, et al. In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:4194–9.?
5��、Cremades N, et al. Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of alpha-synuclein. 2012;149:1048–59.?
6��、Danzer KM, et al. Different species of alpha-synuclein oligomers induce calcium influx and seeding.?J Neurosci.?2007;27:9220–32.?
7��、Tanaka M, et al. Aggresomes formed by alpha-synuclein and synphilin-1 are cytoprotective.?J Biol Chem. 2004;279:4625–31.?
8����、Polymeropoulos, M. H. Mutation in the -Synuclein Gene Identified in Families with Parkinson’s Disease.?Science, 1998;276(5321), 2045–2047. doi:10.1126/science.276.5321.2045?
9、Ki C.S. Stavrou E.F. Davanos N. Lee W.Y. Chung E.J. Kim J.Y. Athanassiadou A. The Ala53Thr mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene in a Korean family with Parkinson disease.?Clin Genet.?2007 May;71(5):471-3.?
10�、Conway, K.E., Harper, J.D., & Lansbury, P.T. Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant α-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease.?Nat Med. 1998, 4(11):1318-20?
11�����、Flagmeier, P. et al. (2016). Mutations associated with familial Parkinson’s disease alter the initiation and amplification steps of α-synuclein aggregation.?PNAS. 113(37):10328-10333.?
12��、Lashuel, H.A., Petre, B.M, Wall, J. et al. α-Synuclein, Especially the Parkinson’s Disease-associated Mutants, Forms Pore-like Annular and Tubular Protofibrils.?J Mol Biol.?2002 Oct 4;322(5):1089-102?
13���、Coskuner, O., Wise-Scira, O. Structures and Free Energy Landscapes of the A53T Mutant-Type αSynuclein Protein and Impact of A53T Mutation on the Structures of the Wild-Type αSynuclein Protein with Dynamics.?ACS Chem. Neurosci.?2013, 4, 1101??
14�、Russel, R., Eliezer, D. Residual structure and dynamics in Parkinson’s disease-associated mutants of alpha-synuclein.?J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 7;276(49):45996-6003.?
?
?
詳情請聯(lián)系StressMarq全國授權(quán)代理-欣博盛生物科技?
全國服務(wù)熱線: 4006-800-892???????郵箱: market@neobioscience.com???
深圳: 0755-26755892???????北京: 010-88594029? ? ? ???
上海: 021-34613729?????????廣州:18024516375????????????
代理品牌網(wǎng)站: www.smblzp.com???
自主品牌網(wǎng)站: www.neobioscience.net?
糖型分析網(wǎng)站:www.glycan-analysis.com??